TUTORIAL
Me-miRNA: Cassava microRNAs collection
A collection of landscape microRNAs and their target genes in cassava (Me-miRNA) based on cassava genome version 4.1
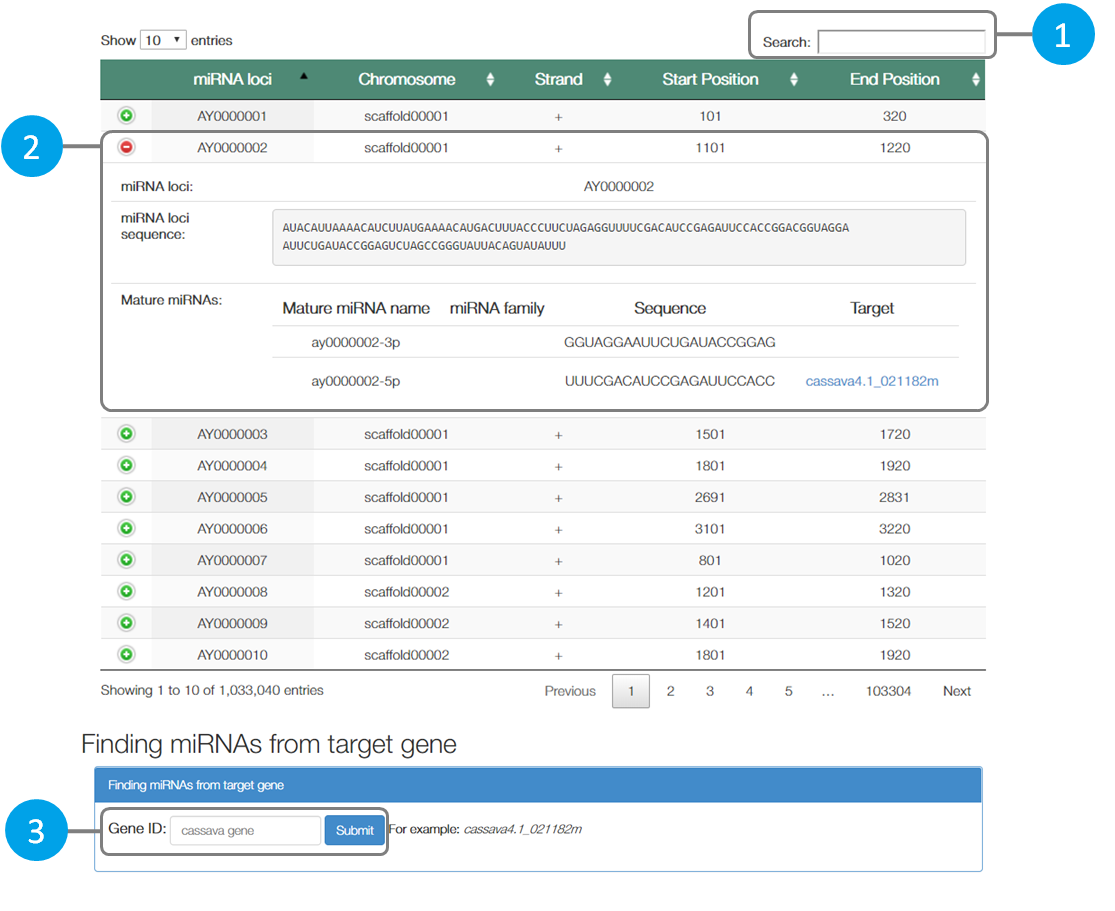
1 |
Search miRNA loci and location |
|---|---|
2 |
Display information of particular miRNA loci |
3 |
Search miRNA loci by using gene target on Phytozome ID |
Description of terminology
| miRNA loci | : A region of cassava genome which contains a predicted miRNA or group of miRNAs. It's compatible to "miRNA gene" or "primary miRNA". The symbol of miRNA loci herein comprises "AY" as a prefix and 7 digit numbers (for example, "AY0000001") |
|---|---|
| mature miRNA | : Functional parts of miRNA loci that are able to bind miRNA targets resulting in miRNA degradation or inhibition. Mature miRNAs herein are structural predicted from stem loop structure(s) on miRNA locus. One miRNA locus can contain more than one mature miRNA. Therefor, the symbol of mature miRNA herein comprises "ay" as a prefix and the same 7 digit-number as their miRNA loci (for example, "ay0000001"). In case of more than one miRNA in miRNA locus, the symbol will be added "." and number, for example "ay0000001.1" and "ay0000001.2". The symbol will be added "-5p" or "-3p" if mature miRNAs are from both arms of duplex were predicted to function (for example, "ay0000001-5p" and "ay0000001-3p"). |
| Family | : A group of mature miRNAs that contain the similar sequences. |
| Mature miRNA sequence | : Sequences of predicted mature miRNA |
| Chromosome | : Location of predicted miRNAs in cassava genome version 4.1 (i.e., chromosome number, scaffold number) based on Phytozome version 11 |
| Start | : Started position of predicted mature miRNA in cassava genome version 4.1 based on Phytozome |
| End | : Ended position of predicted mature miRNA in cassava genome version 4.1 based on Phytozome |
| Strand | : DNA strand (sense (+) or antisense (-)) in cassava genome version 4.1 based on Phytozome |